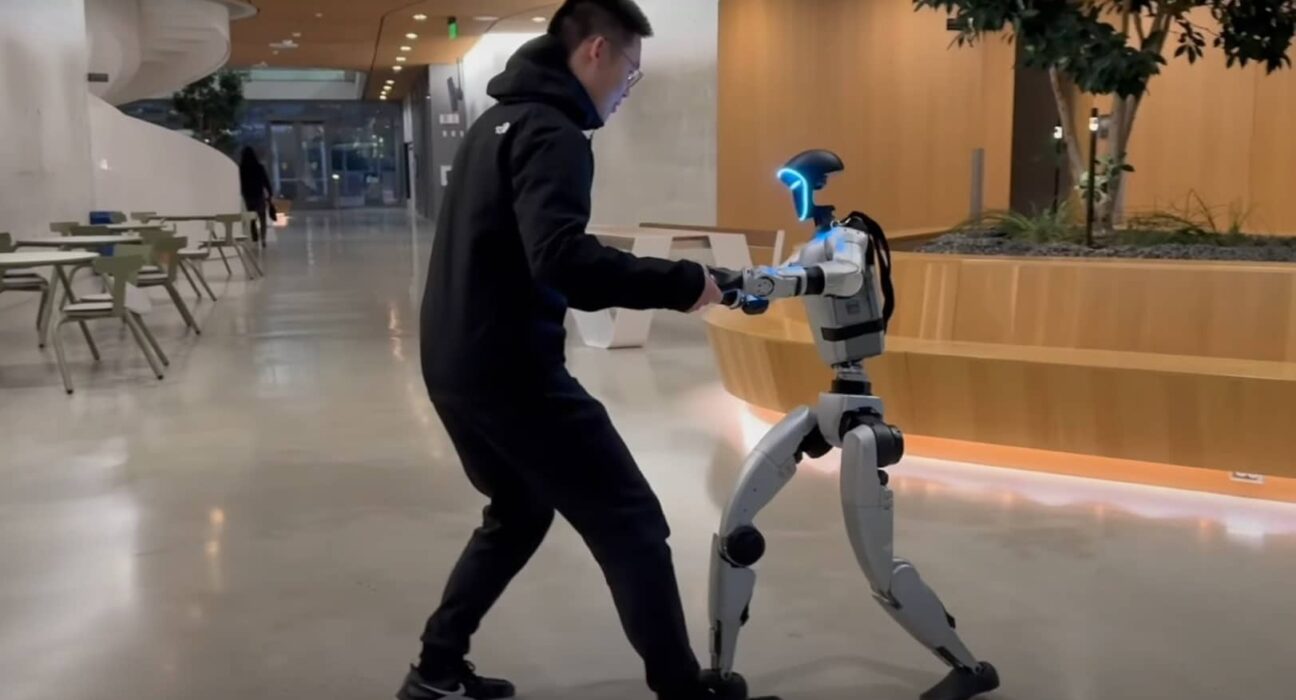
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have developed an AI-powered robot capable of performing the Waltz by mirroring the movements of a human partner. Remarkably, the robot managed to navigate the ballroom dance floor without stepping on any toes.
The team created the robot by first developing an AI model trained on human motion capture data. They integrated this model into two bipedal Unitree G1 robots. Using another AI system, these robots analyzed the motions of humans in their vicinity and mimicked those movements in real time. The outcome was a humanoid robot capable of walking, dodging, squatting, and dancing, all by copying human actions.
Teaching Robots to Move Organically
While robotic stunts and choreographed routines are nothing new—think of robots doing backflips or synchronized dances—this project took a different approach. Instead of relying on pre-programmed scripts, the researchers aimed to teach a robot to learn movements in a more organic manner.
To achieve this, the team developed an AI model called ExBody2, trained using a large database of human motion capture data. In a simulated environment, the model underwent reinforcement learning to understand how to articulate and coordinate the various parts of a robot’s body. Once trained, ExBody2 was integrated into robots equipped with cameras and another AI model designed to process real-world physical data.
This setup allowed the robot to compare observed human movements with its baseline training, enabling it to replicate actions almost instantly. Videos of the robot in action showcase its ability to sidestep, draw circles with its arms, squat, throw punches, and even attempt dance moves.
The Benefits of Adaptable Robots
What sets this project apart is the adaptability of the robots. Unlike other systems that require entirely new training datasets to perform different actions, this approach enables robots to learn and mimic movements dynamically. The short delay—about one second—between observing a motion and replicating it highlights the efficiency of the design.
By focusing on real-time adaptability, researchers are paving the way for more versatile robots that can seamlessly interact with humans in various settings, from dance floors to more practical applications in the future.